Fatigue analysis according to ASME VIII Div.2
- Posted by: Javier Martín
- Category: Static Equipment
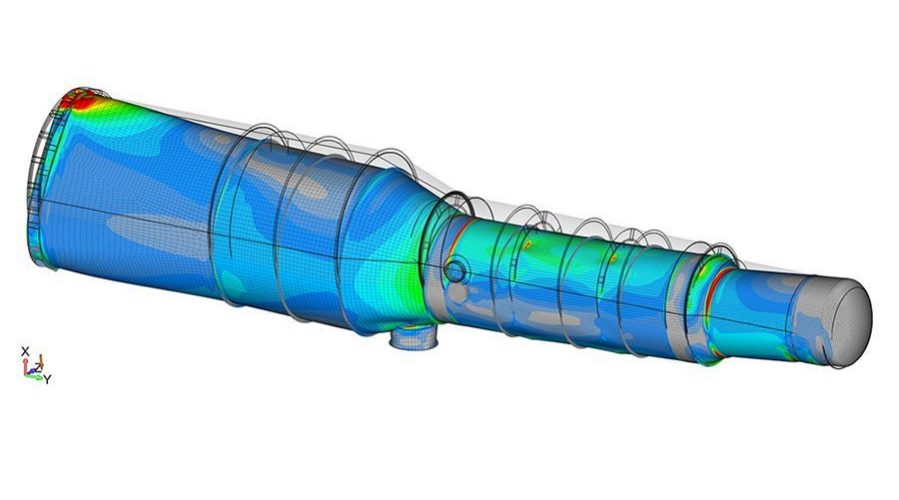
Fatigue analysis is often more demanded for Pressure Vessels and Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers (S&T). Operating conditions involving pressure and/or temperature cycles could result in a fatigue analysis requirement.
Previous to perform a fatigue analysis is necessary to run screening criteria in order to check according to ASME VIII Div. 2 Ap. 5.5. if it is required. The screening criteria shall consider the complete operational conditions.
The first step is to analyse the temperature and pressure cycles applying any of the available methods to define the effective cycles. Using the method “Rain flow analysis”, the peaks and valleys are identified, and consequently the effective number of cycles (full cycles).
Once the total number of cycles are calculated (usually the operation cycle comprises some effective cycles, and the total shall be considered for the screening), the Ap. 5.5 of ASME can be applied. There are two available methods: A and B. both are equivalents, but method A is slightly easier and faster for screening criteria determination. Please note that method A can be used for materials with a specified minimum tensile strength that is less than or equal to 552 MPa (80,000 psi).
Using the method A, the pressure cycles, temperature cycles and the use of different materials (thermal expansion coefficients could be different, and this affects the screening) shall be considered and the contribution of all of them will be compared with the values shown on table 5.9. Depending on the construction of the affected parts (integral or non-integral construction), the sum of all contributions before calculated shall not be greater than the values indicated in order to satisfy the requirement for not performing the fatigue analysis.
To perform a fatigue analysis, a finite element analysis can be used modelling each part of the equipment.
The following fatigue analysis can be studied:
- Fatigue assessment: elastic stress analysis and equivalent stresses
- Fatigue assessment: elastic-plastic stress analysis and equivalent strains
- Fatigue assessment of welds: elastic analysis and structural stress
- Ratcheting assessment: elastic stress analysis
- Ratcheting assessment: elastic-plastic stress analysis
If you want to know more:
ASME VIII | Design of Pressure Vessels
TEMA | Design of Shell & Tube Heat Exchangers



 WhatsApp
WhatsApp