Planning consists of defining each of the steps necessary to achieve small accomplishments towards a larger goal. Planning makes it possible to prevent problems that may arise or, failing that, to have time to resolve and overcome any setbacks that arise from what has been established.
It is a decision-making process to achieve a desired future, taking into account the current situation and the internal and external factors that may influence the achievement of objectives.
It is usually associated with a work or business environment, but it is recognized that it is possible to apply it to any environment such as political, family, social, economic, governmental, educational or any other.
In real terms, planning is as simple as answering the following questions
What? How? Who? and When?
In the end, the difficulty of this process is always given by the type of project on the table. Planning a weekend getaway or a family reunion is not the same as planning an engineering or business project.
A project is a temporary effort to create a unique product, service or result, and to make it a reality it must be planned in advance.
There are different types of planning and different ways of doing it, as well as many planning tools available.
The right way to plan any project should be step-by-step. Start with the most important, define the objective and follow an established order. In addition, it is advisable to do it in advance with enough time, to fit each person, resource and need in the right place.
Thus, the planning process is continuous and iterative, subject to modifications, and does not end until the very moment the project comes to an end.
Steps to plan a project
- Define the objective.
The first question to ask is: what do we need? The answer is the objective. Everything else will depend on its definition: tasks, deadlines, costs? That is why the planning process must start there.
- Establish the scope.
The scope of a project is all the work to be done and the necessary resources. In other words, what is essential for it to be executed.
- Identify resources, costs and risk.
The most important resources for carrying out projects are human resources. Everything must be included in the planning, as well as the costs of each resource, which can be fixed (office rent) or variable (computer repairs). And, of course, it is important not to forget to identify possible risks during start-up, such as, for example, the sick leave of a professional or server failures.
- Analytical work structure.
AWBS (Analytical Work Breakdown Structure) or WBS (Work Breakdown Structure) is the way to organize the work to be done. They are usually in the form of a conceptual map in descending order, and cover from the planning of the project to its closure.
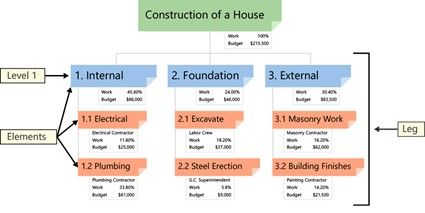
- Breakdown of tasks.
Every project should be able to be broken down into measurable and tangible tasks and subtasks, with an assigned responsible party that is incorporated into the planning. In other words, task breakdown consists of specifying what needs to be done, who does it and when. The more detailed the better.
- Timeline of the project.
This involves including all the activities of the theProject in a bar chart that shows the deadlines, who is responsible for each task and how it evolves over time.
Planning for whom?
We can plan projects for:
- Production: Oriented to produce a good or service according to a determined objective.
- Social Projects: Oriented to improve people’s quality of life.
- Educational Projects: For the formation of other people.
- Community: Directed to people and they participate in the project.
- Research: Oriented to experimentation for innovation.
- Personal: Oriented to personal and individual objectives.
In conclusion, the application of planning and its methodology is important for any project regardless of its origin or magnitude.
If you want to know more:




 WhatsApp
WhatsApp